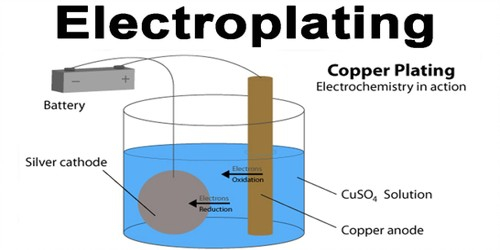
Overview:
Electroplating is a sophisticated surface finishing technique used to deposit a layer of metal onto a substrate through electrolysis. This process enhances the substrate’s properties, providing improved corrosion resistance, durability, conductivity, and aesthetic appeal across various industries.
Electroplating Process:
Preparation and Cleaning:
- Surface Preparation: Substrates undergo meticulous cleaning to remove contaminants and ensure proper adhesion of the plated metal.
- Pre-plating Treatment: Some substrates require pre-treatments like etching or activation to enhance adhesion.
Electroplating Bath and Deposition:
- Electroplating Bath: Consists of a solution containing metal ions, anodes, and electrolytes tailored for specific metals.
- Deposition: Electrical current is passed through the bath, causing metal ions to deposit onto the substrate’s surface, forming a uniform layer.
Metal Varieties and Applications:
- Tin Plating: Provides corrosion resistance and solderability, commonly used in electronic components and food packaging.
- Silver Plating: Offers high electrical conductivity, utilized in electronics, contacts, and decorative applications.
- Nickel Plating: Provides wear resistance and durability, employed in automotive parts, engineering, and decorative finishes.
- Other Metals: Electroplating extends to various metals like gold, copper, zinc, and alloys for specific industrial needs.
Precision and Industry Standards:
Thickness and Specifications:
- Plating Thickness: Controlled with precision, adhering to specifications typically measured in micrometers (μm) or mils (1 mil = 25.4 μm).
- ASTM Standards: Conformance to ASTM B standards defining thickness and quality parameters for specific electroplated metals.
Adherence and Durability:
- Adhesion Strength: Electroplating ensures strong adhesion between the plated layer and substrate, enhancing durability and longevity.
- Industry-specific Requirements: Compliance with industry-specific standards for adhesion, such as MIL-STD for military applications.
Quality Control and Environmental Considerations:
Quality Assurance:
- Quality Inspection: Employing methods like thickness measurement, adhesion tests, and visual inspections to ensure plating conformity.
- Statistical Process Control (SPC): Monitoring plating parameters to maintain consistent quality and adherence to specifications.
Environmental Impact:
- Waste Management: Electroplating facilities implement measures to mitigate environmental impact by recycling and proper disposal of plating chemicals.
Electroplating Techniques stand as versatile methods for enhancing substrate properties and appearance across a spectrum of industries. Their precision control, adherence to standards, and environmental considerations ensure the production of high-quality plated components crucial for various applications.