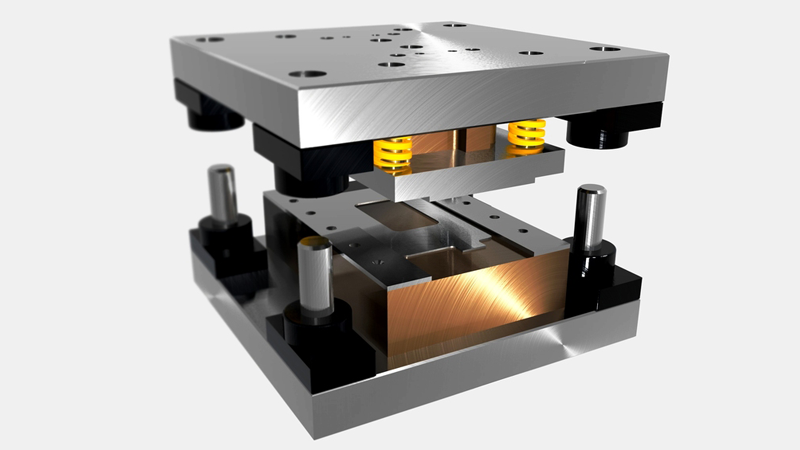
Overview:
In-house Die Fabrication is a specialized process integral to manufacturing precision components across industries. It involves the creation of custom dies, molds, and tooling used in various manufacturing methods like stamping, forging, and extrusion to produce intricate parts with consistent quality.
Die Fabrication Process:
Design and Development:
- CAD/CAM Software: Engineers utilize computer-aided design (CAD) and computer-aided manufacturing (CAM) software to create precise die designs.
- Tool Path Optimization: CAM software optimizes tool paths for efficiency and accuracy in the machining process.
Machining Techniques:
- Precision Machining: Employs various machining methods like milling, turning, and EDM (Electrical Discharge Machining) to shape die materials.
- Tolerances: Achieves tight tolerances, often within microns (μm), critical for creating parts with exact specifications.
Material Selection and Treatment:
- Tool Steels and Alloys: Die materials like tool steels (e.g., D2, A2) or carbide alloys selected for wear resistance and durability.
- Heat Treatment: Heat treatment processes (quenching, tempering) applied to enhance hardness and toughness of die materials.
Precision and Industry Standards:
Accuracy and Tolerances:
- Micro-Tolerance Machining: In-house die fabrication achieves exceptional precision, meeting tolerances as low as 5 microns (μm) or less.
- Compliance with Standards: Adherence to industry standards such as ISO 9001 for quality management and specific tolerances defined by sectors like automotive (e.g., ISO/TS 16949).
Tool Life and Maintenance:
- Tool Durability: Fabricated dies designed for extended tool life, minimizing wear and ensuring consistent part quality over multiple runs.
- Maintenance Protocols: Regular maintenance schedules and inspections to maintain die integrity and performance.
Applications and Quality Assurance:
Diverse Applications:
- Stamping and Forming: Used in metal stamping for automotive components, precision-formed parts in electronics, and complex shapes in aerospace.
- Injection Molding: Applied in manufacturing plastic parts with intricate geometries and tight tolerances.
Quality Control:
- First Article Inspection (FAI): Thorough inspection of initial parts to verify conformance to specifications before mass production.
- Statistical Process Control (SPC): Implementing SPC methods to monitor and maintain consistent quality throughout production runs.
In-house Die Fabrication stands as a cornerstone of precision manufacturing, facilitating the creation of intricate parts with exacting specifications across diverse industries. Its integration of advanced techniques, stringent quality controls, and adherence to standards ensures the consistent delivery of high-quality components vital to modern engineering.