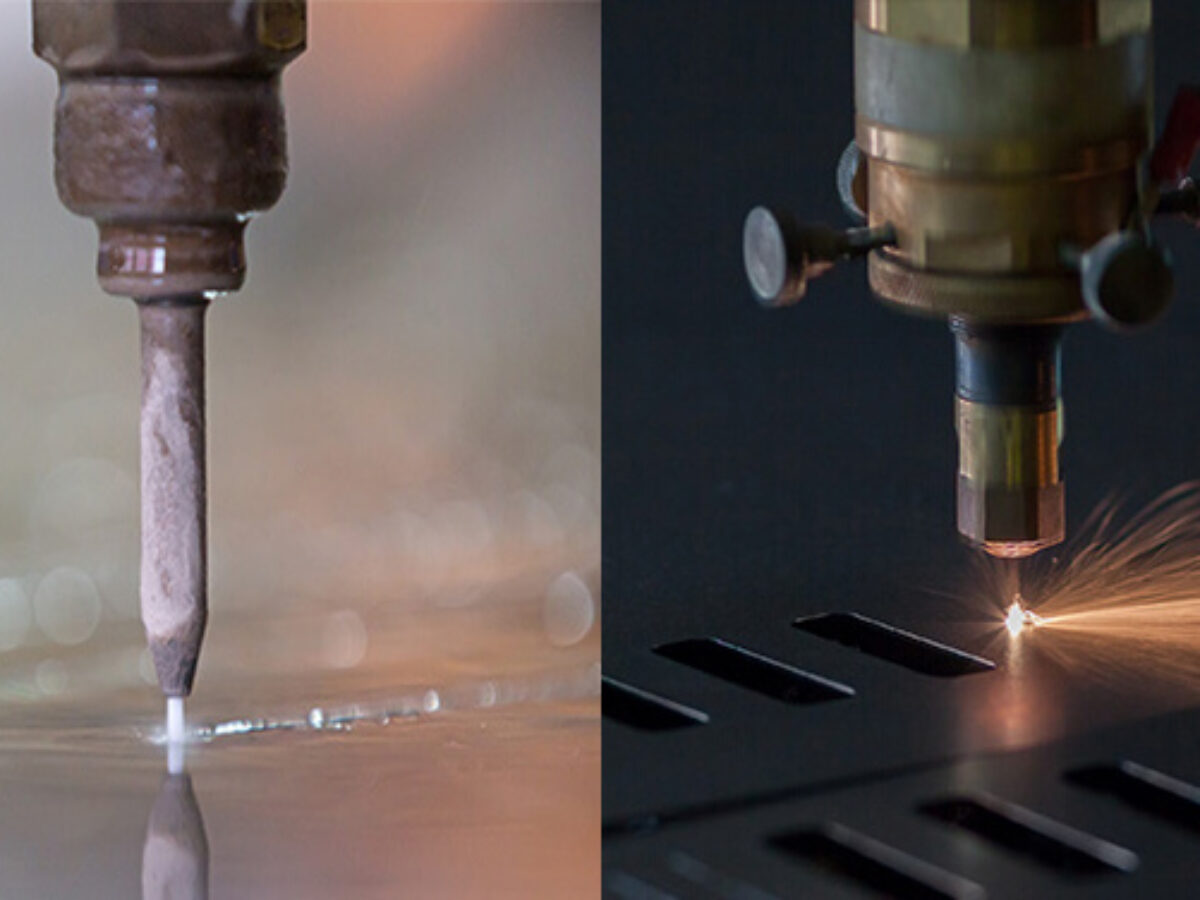
Overview:
Laser cutting and abrasive cutting are advanced machining processes used to precisely cut or shape materials with high accuracy and minimal material waste. These techniques employ focused energy or abrasives to slice through various materials, offering versatility in creating intricate designs and precise cuts across diverse industries.
Laser Cutting Process:
Laser Technology:
- Focused Laser Beam: Utilizes a high-energy laser beam focused through lenses or mirrors to melt, burn, or vaporize materials along a predetermined path.
- Types of Lasers: Includes CO2 lasers, fiber lasers, and neodymium lasers, each suitable for specific materials and thicknesses.
Material and Precision:
- Material Versatility: Cuts metals, plastics, wood, glass, and composites with high precision and intricate detail.
- Precision and Accuracy: Achieves exceptional precision, often within a few thousandths of an inch, ensuring fine, clean cuts.
Applications:
- Industrial Manufacturing: Utilized in automotive, aerospace, electronics, and sheet metal fabrication for precise component production.
- Art and Design: Embraced by artists and designers for crafting intricate patterns and designs in various materials.
Abrasive Cutting Process:
Abrasive Techniques:
- Waterjet Cutting: Utilizes a high-pressure stream of water mixed with abrasive particles to cut through materials.
- Abrasive Wheel Cutting: Employs rotating abrasive wheels to cut metals, ceramics, and other materials.
Versatility and Materials:
- Versatile Material Cutting: Cuts metals, stones, glass, ceramics, and composites, offering versatility in various industries.
- Complex Shapes: Allows for cutting complex shapes and intricate patterns with minimal material wastage.
Applications:
- Industrial Cutting: Widely used in manufacturing, construction, and fabrication industries for precise and clean cutting of materials.
- Custom Fabrication: Applied in custom machining and fabrication for creating specialized components and prototypes.
Precision and Quality Control:
Tolerances and Edge Quality:
- Tight Tolerances: Achieves tight tolerances, often within fractions of a millimeter, ensuring accurate part dimensions.
- Edge Quality: Provides clean, burr-free edges with minimal heat-affected zones, maintaining material integrity.
Quality Assurance:
- Real-time Monitoring: Incorporates real-time monitoring systems to ensure cutting precision and consistency during operations.
- Post-Cutting Inspection: Conducts inspections to verify dimensions, edge quality, and adherence to specifications.
Laser Cutting and Abrasive Cutting stand as advanced machining techniques offering high precision, versatility, and efficiency in producing intricate designs and precise cuts across various materials. Their ability to deliver fine detailing and minimal material wastage makes them vital in modern manufacturing and design.