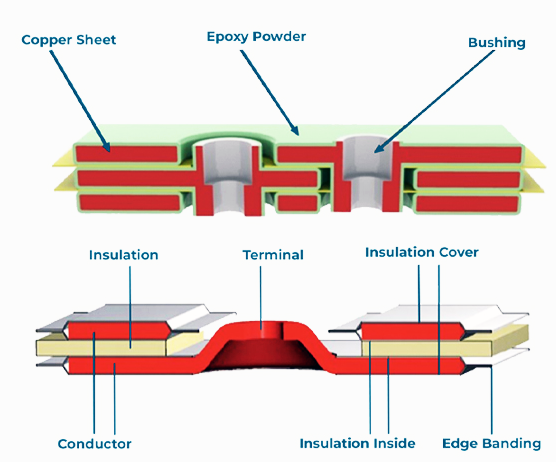
Overview:
Multi-layer lamination and insulation fabrication involve the assembly of multiple material layers to create composite structures with specific properties. These techniques employ precise bonding and layering methods to produce materials with enhanced strength, insulation, and performance tailored to various industrial needs.
Multi-layer Lamination Process:
Layer Assembly:
- Material Selection: Choosing diverse materials like films, foils, fabrics, or composites based on their properties and intended application.
- Layer Arrangement: Precise arrangement and stacking of materials based on desired properties and performance requirements.
Bonding and Lamination:
- Adhesive Bonding: Applying adhesives or bonding agents between layers to create a strong and durable bond.
- Lamination Techniques: Utilizing heat, pressure, or adhesives to fuse layers together, ensuring uniformity and structural integrity.
Customization and Forming:
- Die-Cutting or CNC Machining: Shaping laminated materials into specific shapes or dimensions as per design requirements.
- Thermoforming: Applying heat and pressure to mold laminated materials into 3D forms or contours.
Insulation Fabrication Process:
Insulation Material Assembly:
- Insulation Selection: Choosing materials like polymers, ceramics, or foams known for their insulating properties.
- Layered Assembly: Arranging multiple insulation layers to create effective barriers against heat, sound, or electrical conductivity.
Encapsulation and Coating:
- Encapsulation Methods: Sealing insulation layers within protective coatings or films to enhance durability and resistance to environmental factors.
- Coating Applications: Applying protective coatings for added mechanical strength or resistance to moisture and chemicals.
Types and Applications:
Types of Multi-layer Lamination:
- Polymer Laminates: Combining polymer films for packaging, barrier materials, or flexible electronics.
- Metal-Polymer Composites: Forming conductive or shielding materials used in electronics or aerospace applications.
Diverse Insulation Applications:
- Electrical Insulation: Used in electrical equipment, cables, and circuits to prevent electrical leakage or short circuits.
- Thermal Insulation: Applied in construction, HVAC systems, and industrial processes to minimize heat transfer.
Precision and Quality Assurance:
Bond Strength and Consistency:
- Bond Testing: Conducting peel tests or shear tests to ensure strong and consistent bonding between layers.
- Thickness Control: Ensuring uniform layer thickness through precise lamination and coating techniques.
Quality Control Measures:
- Visual Inspection: Inspecting for delamination, air pockets, or defects that may compromise material integrity.
- Performance Testing: Conducting insulation resistance, dielectric strength, or thermal conductivity tests to validate insulation properties.
Multi-layer lamination and insulation fabrication techniques offer a versatile means of creating composite materials with tailored properties. Their ability to combine various materials and assembly methods makes them crucial in achieving specific performance requirements across industries.