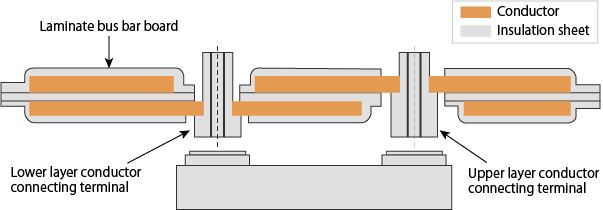
Laminated Bus Bars represent an innovative approach to electrical conduction, offering a combination of efficiency, compact design, and enhanced thermal performance. These bars, composed of multiple layers of conductive materials insulated and bonded together, provide unique advantages in various electrical applications.
Technical Specifications:
Construction:
- Layered Structure: Typically constructed by bonding together multiple layers of conductive materials (copper, aluminum) with insulating layers (usually made of high-dielectric materials like epoxy resin or Mylar film).
- Materials: Conductive layers may consist of copper, aluminum, or their alloys, chosen for their electrical properties, while insulating layers ensure electrical isolation between conductive layers.
Electrical and Mechanical Properties:
- Conductivity: Laminated Bus Bars maintain high electrical conductivity similar to solid copper or aluminum bars, depending on the material used in the conductive layers.
- Insulation Strength: The insulating layers offer excellent dielectric properties, ensuring effective isolation between conductive layers.
- Mechanical Strength: Varies based on the materials used and bonding techniques employed.
Thermal Performance:
Heat Dissipation:
- Laminated Bus Bars’ design allows for improved heat dissipation due to increased surface area and the use of insulating layers that separate conductive layers, reducing the risk of hotspots.
Thermal Conductivity:
- The thermal conductivity of laminated bus bars is influenced by the materials used in the conductive layers, with copper-based laminates offering higher thermal conductivity compared to aluminum-based ones.
Manufacturing and Applications:
Manufacturing Processes:
- Laminated Bus Bars are fabricated through precision machining, bonding, and insulating techniques to create layered structures of varying thicknesses and dimensions.
- Techniques such as CNC machining and lamination processes ensure precise construction and insulation.
Applications:
- Power Electronics: Widely used in inverters, converters, and power supply systems due to their high current-carrying capacity and compact design.
- Automotive and Aerospace: Utilized in vehicle power systems and aircraft electrical systems for their efficiency and space-saving characteristics.
- Renewable Energy Systems: Applied in solar inverters and wind turbine systems where efficient power transmission and heat dissipation are crucial.
Advantages and Considerations:
Advantages of Laminated Bus Bars:
- Compact Design: Laminated structure allows for reduced space requirements compared to traditional solid bus bars.
- Improved Thermal Performance: Enhanced heat dissipation capabilities owing to increased surface area and insulation between conductive layers.
Considerations:
- Manufacturing Complexity: The production of laminated bus bars requires precise bonding and insulating processes, impacting manufacturing complexity and costs.
- Material Selection: Choosing appropriate materials for conductive and insulating layers is critical for achieving desired electrical and thermal properties.
Laminated Bus Bars stand as a sophisticated solution in electrical systems, offering a balance between electrical efficiency, compactness, and enhanced thermal performance. Their intricate design, precise manufacturing, and versatility underscore their significance in various electrical and power distribution applications.